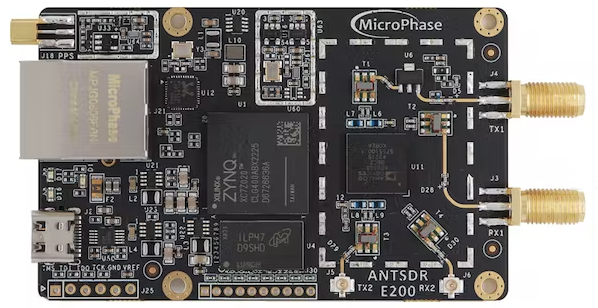
Open source software-defined radio board combines AMD Xilinx ZYNQ-7020 with Arm processors and FPGA resources.
Software-defined radio (SDR) hardware based on the AMD Xilinx ZYNQ-7020 with two full-duplex channels and a 20MHz bandwidth is about to be released by FPGA designer Chaochen Wei. an ANTSDR-E200.
Wei describes the idea as being "influenced by [ADALM-PLUTO] PlutoSDR and Ettus USRP B200." "Visually, having an ANTSDR-E200 is equal to simultaneously owning a PlutoSDR and a USRP B200. The ANTSDR-Ethernet E200's interface makes it simple to deploy the device to the distant end via a network switch."
The AMD Xilinx ZYNQ-7020 system-on-chip powers the majority of the board. It combines two Arm Cortex-A9 MPCore processor cores with speeds of up to 866MHz with an Analog Devices AD9363 field-programmable gate array (FPGA) with 85k logic cells, 4.9Mb of block RAM, 220 DSP slices, and up to 200 input/output (IO) pins. Because Wei has transferred the open-source firmware from the PlutoSDR project to the ANTSDR-E200, everything should be fairly familiar to users of that project.
Along with the radio-frequency integrated circuit (RFIC), which provides four channels—two receive and two transmit, capable of operating independently or as two full-duplex channels—the board also includes a gigabit Ethernet port for remote operation, an offload engine to increase throughput, 512MB of DDR3 memory, and 256MB of QSPI flash. The board is advertised as having a frequency range of 325MHz to 3.8GHz, sampling at 61.44 MSPS, and a bandwidth of 20MHz.
Both the converted PlutoSDR firmware and a variant of the Ettus UHD firmware, as well as a "reduced version of [the] schematic" in PDF format, have been made available on GitHub by Wei's company, MicroPhase, under the reciprocal GNU General Public License 3.
Though Wei intends to start a crowdfunding campaign via Crowd Supply soon, no specific date had been specified at the time of writing, so anyone hoping to get their hands on a board would have to wait.